You have a powerful gaming laptop and a new VR headset. You are ready for immersive worlds. Yet, you experience stuttering, low frame rates, and a subpar experience. This is a common issue for many people. Laptops operate under unique power and thermal constraints compared to desktops.
Optimizing your machine is not about one single fix. It is a process of systematic adjustments across your hardware, operating system, and software. You will learn the specific steps to get smooth, high-fidelity virtual reality performance from your gaming laptop. We will cover everything from driver settings to hidden Windows options.
Getting your laptop VR-ready requires attention to detail. Many default settings are configured for battery life or quiet operation, not maximum performance. By following these instructions, you direct your laptop’s full potential toward your VR experience. Prepare to see a significant improvement in clarity and smoothness.
Prepare Your Hardware and System
Before you adjust any software settings, you must prepare your physical hardware and core system software. These foundational steps ensure your laptop has the stability and resources needed for demanding VR applications. A poor setup here will undermine all other optimization efforts.
Your laptop’s cooling system is your first priority. VR pushes your processor (CPU) and graphics card (GPU) to their limits, generating substantial heat. Laptops have compact cooling systems that work hard to dissipate this heat. If they fail, your components will “thermal throttle,” reducing their performance automatically to prevent damage. This is a primary cause of stuttering in VR.
Proper software setup is equally important. Outdated graphics drivers lack critical performance improvements and bug fixes for new VR games. Your operating system also needs to be told to prioritize gaming performance over power efficiency. These initial steps create the stable base necessary for advanced tuning.
Ensure Optimal Cooling and Airflow
First, place your laptop on a hard, flat surface. Never use your gaming laptop on a bed or carpet for VR. Soft surfaces block the air intake vents, usually on the bottom of the machine, causing components to overheat quickly. This starves your system of cool air.
For better cooling, elevate the back of the laptop. This increases the space underneath for air intake. You can use a dedicated laptop stand or a simple object like a book. Many gaming laptop stands also include built-in fans. These fans push more cool air into the laptop’s intake vents, actively aiding your system’s own fans.
Finally, clean your laptop’s fans and heatsinks. Dust buildup acts as an insulator, trapping heat and making your cooling system less effective. If you are comfortable doing so, open your laptop’s bottom panel and use compressed air to clear out the dust. If not, a computer repair shop can perform this service for you.
Update Your Graphics Drivers
Your GPU is the single most important component for VR performance. Graphics card manufacturers like NVIDIA and AMD frequently release driver updates. These updates often contain specific optimizations for the latest VR games and headset software, resulting in higher frame rates and fewer bugs.
You should always perform a “clean installation” of your graphics drivers. This process removes all old driver files before installing the new ones, preventing potential conflicts or bugs from carrying over. You can use the clean install option within the NVIDIA or AMD driver installer. For an even more thorough process, experts recommend a tool called Display Driver Uninstaller (DDU) to completely wipe old drivers before an update.
Pro Tip: Check for new graphics drivers at least once a month. Also, check before playing a newly released major VR title. Developers work with NVIDIA and AMD to have performance-enhancing “Game Ready” drivers available at launch.
Connect Directly to the Correct Port
This step is critical and often overlooked. Most gaming laptops have multiple video output ports. You need to connect your VR headset to the port that is wired directly to your dedicated GPU, not the integrated graphics on your CPU. This bypasses the integrated GPU and reduces latency, a critical factor for a comfortable VR experience.
The DisplayPort or a USB-C port with DisplayPort capability is connected directly to the dedicated GPU. The HDMI port sometimes routes through the integrated graphics. Check your laptop’s user manual or the manufacturer’s website to confirm which port offers a direct connection. For NVIDIA laptops, you can check the NVIDIA Control Panel under the “Configure Surround, PhysX” tab to see a diagram of your port layout.
Graphics Card Settings
Your graphics control panel is the command center for your GPU. This is where you can override default settings and force your system to prioritize performance for VR applications. The two main control panels are the NVIDIA Control Panel for GeForce GPUs and AMD Radeon Software for Radeon GPUs. We will cover the most important settings for both.
The global settings in your control panel affect all 3D applications. However, for VR, it is best to create application-specific profiles. This allows you to apply aggressive performance settings to your VR games and the SteamVR or Oculus software without affecting the performance of other desktop applications.
You want to configure settings that reduce graphical load without a massive drop in visual quality. Options like texture filtering, power management, and pre-rendered frames have a large impact on the smoothness of your VR experience. Let’s walk through the ideal configuration.
NVIDIA Control Panel for VR
If your gaming laptop has an NVIDIA GeForce GPU, the NVIDIA Control Panel is your primary tool. Right-click on your desktop and select “NVIDIA Control Panel” to open it. Go to Manage 3D settings.
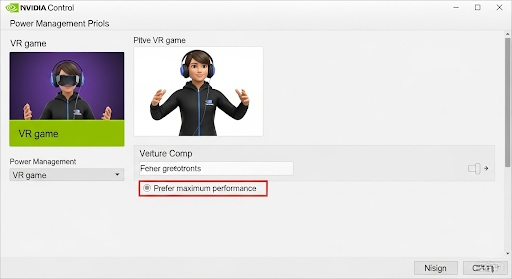
First, select the Program Settings tab. Click “Add” and find the executable for both your VR runtime (like vrmonitor.exe for SteamVR) and the specific VR game you want to optimize. Once you have selected a program, apply these settings for maximum performance:
- Power management mode: Set to Prefer maximum performance. This prevents your GPU from downclocking to save power, ensuring it runs at full speed during VR sessions.
- Low Latency Mode: Set to On. This reduces the number of frames the CPU prepares ahead of the GPU, which can lower input lag.
- Texture filtering – Quality: Set to High performance. This makes a small change to texture sharpness but provides a noticeable performance gain.
- Vertical sync: Set to Off. VR headsets manage their own frame synchronization. V-Sync can interfere with this process, known as reprojection or motion smoothing, and cause stutter.
Apply these settings for each VR game and the SteamVR application itself. This ensures your GPU is always in its highest performance state when you need it most.
AMD Radeon Software for VR
For laptops with AMD Radeon GPUs, you will use the AMD Radeon Software. Right-click your desktop and open it. Navigate to the Gaming tab. Here, you can select specific games to create graphics profiles for, or you can adjust the Global Graphics settings.
Similar to the NVIDIA process, it is best to create profiles for your specific VR games and platforms. Here are the key settings to adjust:
- Radeon Anti-Lag: Enabled. This feature reduces input lag by controlling the pace of the CPU’s work to ensure it does not get too far ahead of the GPU.
- Radeon Chill: Disabled. This feature saves power by limiting frame rates when there is little on-screen movement. This is not desirable for VR, where a consistent high frame rate is essential.
- Wait for Vertical Refresh: Always Off. This is AMD’s version of V-Sync. You must disable it to allow the VR headset’s software to control frame timing.
- Texture Filtering Quality: Set to Performance. This provides a performance uplift with a minimal impact on visual fidelity.
Making these adjustments in the AMD Radeon Software tells your GPU to focus entirely on delivering frames as quickly as possible, which is the main goal for smooth VR.
Fine-Tuning Windows for Peak VR Performance
The Windows operating system has several features that can interfere with or assist VR performance. By default, Windows tries to balance performance with power efficiency and background tasks. For VR, you need to tell it to prioritize your game above all else. These optimizations are simple to implement and provide a stable environment for your VR sessions.
These changes involve modifying power plans, disabling visual effects, and using built-in Windows tools designed for gaming. Each adjustment removes a potential bottleneck, freeing up more CPU and GPU resources for your virtual reality experience. This ensures that background processes are not stealing resources at a critical moment, which would cause a frame drop and visible stutter in your headset.
Activate the Ultimate Performance Power Plan
Windows uses power plans to manage how your computer consumes energy. The “Balanced” plan is active by default on most laptops, which can limit CPU performance to save battery. For VR, you need to use a plan that unleashes your hardware.
Open the Windows Command Prompt as an administrator. Type the following command and press Enter:
powercfg -duplicatescheme e9a42b02-d5df-448d-aa00-03f14749eb61.
This command unhides the Ultimate Performance power plan.
Next, go to Settings, then System, then Power & sleep, and click on “Additional power settings.” You will now see “Ultimate Performance” as an option. Select it. This plan minimizes system latency and ensures your CPU runs at maximum frequency when needed. Remember to always have your laptop plugged into AC power when using this plan, as it will drain your battery very quickly.
Enable Windows Game Mode
Game Mode is a feature in Windows 10 and 11 designed to optimize your system for gaming. When enabled, Windows prioritizes CPU and GPU resources for your game. It also prevents Windows Update from performing driver installations or sending restart notifications in the middle of a gaming session.
To enable it, go to Windows Settings, select Gaming, and then select Game Mode. Make sure the toggle is switched to On. This is a simple but effective way to ensure more of your system’s resources are dedicated to your VR experience.
Disable Unnecessary Background Applications
Many applications run in the background, consuming CPU cycles and memory. Before starting a VR session, close every non-essential application. This includes web browsers, music streaming services like Spotify, and communication apps like Discord or Slack. Even apps running minimized in the system tray can consume resources.
You can use the Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc) to see what is running. Pay special attention to the “Startup” tab. Disable any programs you do not need to launch automatically when you start your computer. This reduces background clutter and ensures your VR game has access to as much RAM and CPU power as possible. Common resource hogs include cloud storage sync clients and software update checkers.
Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling (HAGS)
Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling, or HAGS, is a feature available in modern versions of Windows. It allows your graphics card to manage its own video memory directly, which can reduce latency and improve performance in some situations. The impact of HAGS can vary between systems and games, so it requires testing.
To enable it, go to Settings, then System, then Display. Scroll down and click on “Graphics settings.” Turn on the toggle for Hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling. You will need to restart your computer for the change to take effect. Test your VR performance with HAGS on and off to see which setting provides better results for your specific laptop and headset combination.
Optimizing Your Specific VR Platform
After preparing your hardware and operating system, the next step is to configure the software platform that runs your VR experience. The most common platforms for PC VR on a laptop are SteamVR, Oculus Link (for Meta Quest headsets), and Virtual Desktop. Each has its own set of performance-tuning options.
These settings control the rendering resolution, refresh rate, and the methods used to handle missed frames. Finding the right balance is key. Pushing the resolution too high will cripple your laptop’s performance. Setting it too low will result in a blurry, unappealing image. Your goal is to find the sweet spot that gives you a clear image while maintaining a consistent frame rate.
The target frame rate should match your headset’s native refresh rate. For example, a headset with a 90Hz display needs to run at a steady 90 frames per second (FPS) for a smooth experience. If your laptop cannot maintain this target, the VR platform will engage a feature like motion smoothing or reprojection. These features generate synthetic frames to fill the gaps, which prevents extreme judder but can introduce visual artifacts. A properly tuned system will rely on these features as little as possible.
SteamVR Settings
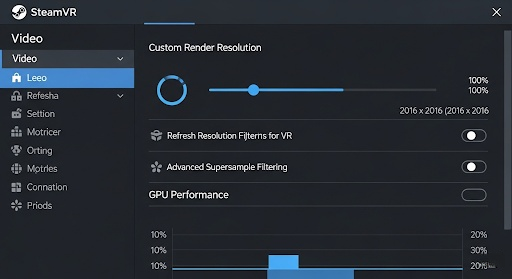
SteamVR is the most widely used platform for PC VR. It has a robust set of video settings that you can adjust globally or on a per-application basis. Open SteamVR and go to Settings, then select the Video tab.
The most important setting here is Render Resolution. By default, it is set to “Auto,” which tries to guess the best resolution based on your GPU. For more control, switch this to Custom. Start at 100%. This corresponds to the native resolution of your headset. If you experience poor performance, try lowering this value to 90% or 80%. This will reduce the load on your GPU significantly.
If your performance is excellent, you can try pushing the resolution above 100% for a sharper image, a technique called supersampling. Also, check the Advanced Settings and look for motion smoothing options. For some users, disabling motion smoothing provides a more consistent experience, even if it means occasional frame drops are more noticeable. Experiment to see what you prefer.
Meta Quest Link / Air Link Settings
If you use a Meta Quest 2, 3, or Pro headset with your laptop via a USB cable (Link) or wirelessly (Air Link), you can adjust performance settings in the Oculus PC app. Open the app, go to Devices, and click on your headset. This will open a panel with Graphics Preferences.
Here, you can adjust two key settings: Refresh Rate and Render Resolution. For the Refresh Rate, you should select a value your laptop can consistently maintain. While 120Hz is an option on some headsets, 90Hz or even 72Hz are more realistic targets for many gaming laptops. A stable 90 FPS is much better than an unstable 120 FPS.
The Render Resolution slider works just like the one in SteamVR. A higher value produces a sharper image but is more demanding on your GPU. Start with the recommended setting for your GPU, which the software displays on the slider. Adjust it up or down based on your performance in-game. A small reduction in render resolution can provide a large boost in frame rate stability.
Virtual Desktop Settings
Virtual Desktop is a popular third-party application for playing PC VR games wirelessly on a Quest headset. It offers its own unique set of streaming and performance settings within its “Streaming” tab.
First, select your Graphics Quality. Options like Low, Medium, High, and Ultra determine the render resolution. Start with Medium or High for a balance of quality and performance. Next is the VR Bitrate. This controls the quality of the wireless video stream. A higher bitrate looks better but requires a very strong Wi-Fi connection and can introduce latency. A good starting point is around 90-100 Mbps for a Wi-Fi 6 connection.
Virtual Desktop also features a performance overlay that shows your frame rate and latency in real-time. Use this tool to diagnose bottlenecks. For instance, if your “Game” latency is high, your GPU is the bottleneck. If your “Network” latency is high, your Wi-Fi connection is the problem. This makes it an excellent tool for fine-tuning your entire setup.
In-Game Settings: The Final Frontier of Optimization
Even with a fully optimized system, the settings within each VR game itself have the largest impact on performance. Every game is different, but they share common graphical settings that you can adjust to find the perfect balance between visual quality and a smooth frame rate.
When you first launch a VR game, do not jump directly into the action. Go straight to the graphics settings menu. Your goal is to disable or lower the most demanding settings first. These “GPU-heavy” effects often provide only minor visual improvements but consume a massive amount of performance.
Always aim to hit your headset’s native refresh rate as a minimum target. If you have a 90Hz headset, your goal is a locked 90 FPS. Use a performance monitoring tool like the one built into SteamVR or a third-party app like FPSVR to watch your frame rate as you adjust settings. Make one change at a time, then test the result. This methodical approach will help you isolate which settings have the biggest performance impact.
Identify and Lower Demanding Settings
Certain graphics settings are known to be particularly demanding on any system. When optimizing a VR game, start by lowering these first:
- Shadows: High-resolution dynamic shadows are extremely taxing on the GPU. Lowering shadow quality from “Ultra” to “Medium” or “Low” can provide a huge performance increase with a minimal visual downgrade.
- Anti-Aliasing (AA): This technique smooths jagged edges. While important for clarity, high levels of AA like MSAA 8x are very costly. Try a less demanding option like MSAA 2x or a post-processing method like FXAA or SMA.
- Ambient Occlusion (AO): This adds soft shadows where objects meet, creating depth. It looks nice but is a non-essential effect. Turning AO off or setting it to a lower quality level can free up significant GPU resources.
- Reflections: Real-time reflections, especially screen-space reflections, are very demanding. Lowering this setting can provide a substantial FPS boost, particularly in scenes with water or shiny surfaces.
Use Per-Game Resolution Scaling
Many modern VR games include their own internal resolution or supersampling slider. This functions independently of the render resolution you set in SteamVR or the Oculus app. If a game has its own resolution scaler, it is often best to set the platform-level resolution (SteamVR/Oculus) to 100% and then use the in-game slider for fine-tuning.
This gives you more direct control over the game’s performance. You might find that one game runs well at 120% internal resolution, while a more demanding title needs to be lowered to 90% to maintain a stable frame rate. This per-game approach is the key to getting the best experience across your entire VR library.
Advanced Tools and Monitoring
To truly master your laptop’s VR performance, you need to see what is happening under the hood. Monitoring tools give you real-time data on your CPU and GPU usage, temperatures, and frame times. This information helps you identify bottlenecks and confirm that your optimizations are working as intended.
A performance bottleneck occurs when one component is holding back the rest of your system. For example, your GPU might be at 100% usage while your CPU is only at 40%. This indicates a “GPU bottleneck,” meaning your graphics card is the limiting factor. In this case, lowering graphical settings is the correct solution. Conversely, if your CPU is at 100% and your GPU is not, you have a “CPU bottleneck,” and you should focus on lowering settings that affect the processor, like physics or object detail.
Using MSI Afterburner and RivaTuner
MSI Afterburner is a powerful free utility that works with GPUs from all brands. It allows you to monitor your hardware in detail. You can track your GPU temperature, clock speed, usage, and VRAM consumption. RivaTuner Statistics Server, which is installed with Afterburner, provides an on-screen display to see this information while you are in-game.
While viewing this data directly in VR is difficult, you can run a game on your monitor in 2D mode with the same settings to get a baseline. Pay close attention to your GPU temperature. If it consistently exceeds 85-90°C, you are likely thermal throttling. This confirms that you need to improve your laptop’s cooling.
FPSVR: The Essential VR Monitoring Tool
For in-headset monitoring, FPSVR is an indispensable tool available on the Steam store. It attaches a small, customizable overlay to your wrist or controller in VR. This overlay displays your current FPS, CPU and GPU frame times, temperatures, and usage percentages.
Watching your frame times is more useful than watching your FPS. Frame time is the time it takes to render a single frame. For 90 FPS, each frame must be rendered in 11.1 milliseconds (ms). If your GPU frame time spikes above this value, you will drop a frame. FPSVR visualizes these frame times with a graph, making it easy to see stutters and identify their cause. This tool allows you to make a settings change in-game and immediately see its impact on performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know if my gaming laptop is VR ready?
To confirm if your gaming laptop is VR ready, check its specifications against the minimum requirements of your VR headset, such as the Meta Quest 3 or Valve Index. Key components are the GPU (NVIDIA RTX 3060 Laptop or better is a good baseline), CPU (Intel Core i7 or AMD Ryzen 7), and at least 16GB of RAM. Also ensure you have the correct video output port (usually DisplayPort 1.4 or a compatible USB-C).
Why is my VR lagging on a good gaming laptop?
Lag or stuttering on a good gaming laptop is often caused by thermal throttling, where the CPU or GPU slows down due to excessive heat. Other common causes include outdated graphics drivers, running VR on the wrong power plan (not “Ultimate Performance”), or having background applications consuming resources. Following a full guide on how to optimize your gaming laptop for VR will address these issues.
Does increasing laptop RAM improve VR performance?
Increasing RAM can improve VR performance if your system currently has less than 16GB. VR applications and games are memory-intensive. Moving from 8GB to 16GB will reduce stuttering and improve loading times. However, if you already have 16GB or more, adding more RAM will likely not provide a noticeable performance increase unless you are running many other applications alongside your VR game.
What are the best NVIDIA settings to optimize a gaming laptop for VR?
The most critical NVIDIA Control Panel settings are setting “Power management mode” to “Prefer maximum performance,” turning “Low Latency Mode” to “On,” setting “Texture filtering – Quality” to “High performance,” and turning “Vertical sync” to “Off.” You should apply these settings specifically for your VR applications and games under the “Program Settings” tab.
How can I reduce motion sickness when optimizing my gaming laptop for VR?
Reducing motion sickness is directly tied to performance. A stable, high frame rate is the most important factor. Follow all optimization steps to eliminate stutter and frame drops, as an inconsistent frame rate is a primary cause of VR sickness. Additionally, ensure your headset’s IPD (interpupillary distance) is set correctly to match your eyes, which helps with focus and reduces eye strain.






